To configure the IM19, it is easiest to open a second instance of PyGPSClient and connect to Pi UART2 (usually /dev/ttyAMA2) at 115200 baud.
We need to configure the IM19 using “AT” commands. PyGPSClient calls these “TTY” commands:
AT+LOAD_DEFAULT
AT+GNSS_PORT=PHYSICAL_UART2
AT+NASC_OUTPUT=UART1,ON
AT+LEVER_ARM2=0.0057,-0.0732,-0.0645
AT+CLUB_VECTOR=0,0,1.865
AT+INSTALL_ANGLE=0,180,0
AT+GNSS_CARD=OEM
AT+WORK_MODE=408
AT+CORRECT_HOLDER=ENABLE
AT+SET_PPS_EDGE=RISING
AT+AHRS=ENABLE
AT+MAG_AUTO_SAVE=ENABLE
AT+SAVE_ALL
In PyGPSClient Preset JSON format, this is:
"ttypresets_l": [
"INIT_PRESETS",
"IM19 Tilt Survey Setup; AT+LOAD_DEFAULT; AT+GNSS_PORT=PHYSICAL_UART2; AT+NASC_OUTPUT=UART1,ON; AT+LEVER_ARM2=0.0057,-0.0732,-0.0645; AT+CLUB_VECTOR=0,0,1.865; AT+INSTALL_ANGLE=0,180,0; AT+GNSS_CARD=OEM; AT+WORK_MODE=408; AT+CORRECT_HOLDER=ENABLE; AT+SET_PPS_EDGE=RISING; AT+AHRS=ENABLE; AT+MAG_AUTO_SAVE=ENABLE; AT+SAVE_ALL",
"IM19 System reset CONFIRM; AT+SYSTEM_RESET",
"IM19 Save the parameters; CONFIRM AT+SAVE_ALL"
],
This will enable the IM19 NAVI ASCII NMEA-format GPFMI message on IM19 UART1. It contains the tilt-compensated pole tip position - once the IM19 is calibrated.
We need to set the LEVER_ARM, CLUB_VECTOR and INSTALL_ANGLE parameters carefully.
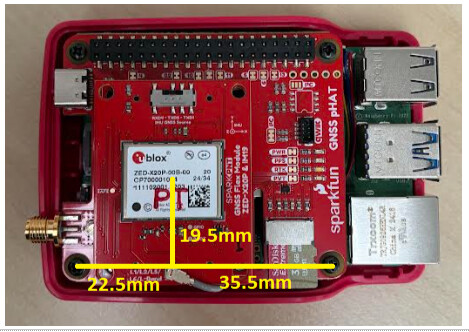
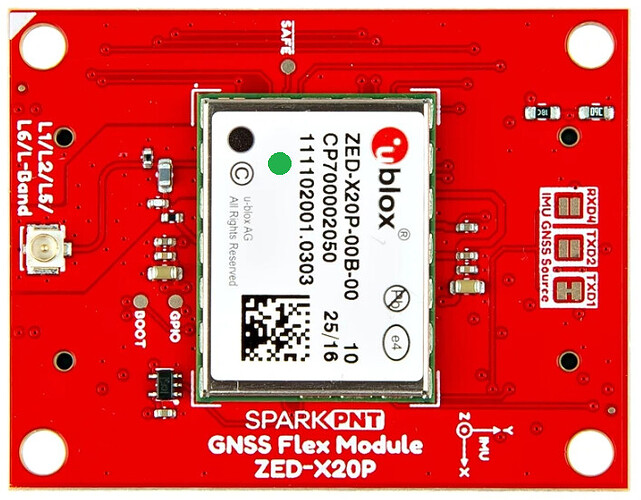
The X20P and IM19 module packages are centred on the centre of the Flex module. On the pHAT, the position relative to the mounting screw holes is:
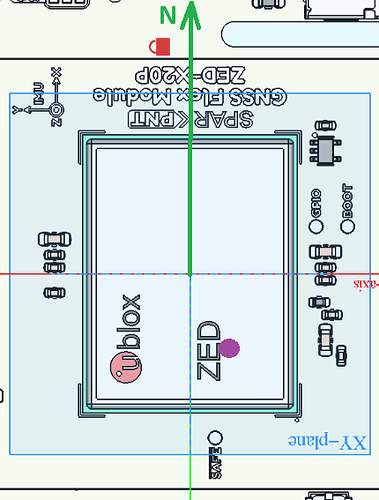
Important note: The IM19 IMU origin is not centred on the centre of the module. Using IMU Coordinates, it is offset by -5.72mm in X, and -2.72mm in Y. The green dot is the IMU origin:
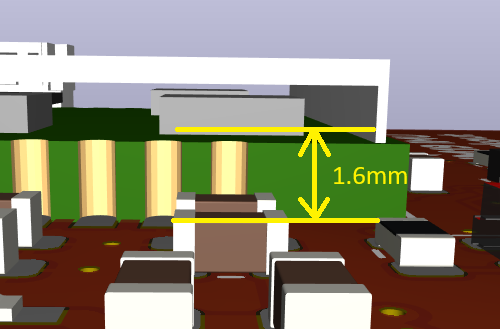
The IM19 Z origin is 1.6mm from the back surface of the Flex Module PCB:
In IMU Coordinates, the top surface of the Flex Module PCB is offset by +3.2mm in Z. 1.6mm for the PCB thickness plus the 1.6mm internal to the IM19.
The antenna reference position (phase centre) can be specified using either the LEVER_ARM=X,Y,Z message, or LEVER_ARM2=X,Y,Z. For LEVER_ARM2, note: “When setting the lever arm parameters by AT+LEVER_ARM2, the lever arm parameters will be internally rotated according to the currently installation angle. Therefore, the lever arm parameters should be measured in the default coordinate system of the module.” If the antenna is “above” the IMU, its Z position is negative for LEVER_ARM2, even though the IMU is flipped. The units are metres.
The CLUB_VECTOR=X,Y,Z message sets the pole length, from the ARP to the pole tip. The units are metres. For a 1.8m pole, the Z offset is +1.80m.
The INSTALL_ANGLE=X,Y,Z defines the rotation (installation angle) of the IMU package. Defining the rotation needs care if more than one rotation is involved. This video by u-blox is really useful here. The units are degrees. The IM19 manual says “Send AT+INSTALL_ANGLE=180,0,0 If the IM19 module is mounted on the back of the GNSS receiver (so the IM19 faces downward instead of upward)”. That is only true if the module has been flipped around the X axis only.
The IM19 manual says:
- “Make sure the end of the RTK pole is placed on the ground and does not move. [Rock] the RTK pole back and forth for 2 to 3 times. The IM19 module will alter the positioning status to initialization complete, and the user can start tilt survey.”
- “If the installation angle has not been calibrated in the factory, when initializing in the first time, you need to rotate the RTK pole by 90° according to the prompt given by IM19 to complete the initialization.”
PyGPSClient has a tool to analyze the GPFMI message Status field: View \ Show IMU Monitor. The calibration is complete when FixRIsOK is observed.
PyGPSClient can extract the Latitude, Longitude and Altitude from the GPFMI message. It is a fun thing to log data from both instances of PyGPSClient. The GNSS data contains the position of the antenna - with no tilt compensation. The IM19 GPFMI data contains the compensated pole tip position.